Application of Generators in Homes: Powering Up Your Living Space Efficiently
Fundamental Principles of Home Generators
Home generators operate on specific principles that allow them to produce electricity efficiently. Understanding how they work can help you make better choices when using these devices at home.
How Generators Produce Electricity
Generators create electricity by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. This process usually involves an engine that runs on fuel, such as gasoline or propane. As the engine runs, it rotates a rotor inside the generator.
This rotation is vital because it helps generate electrical output. The more the rotor turns, the more electricity is produced. You can typically find this electricity output measured in watts, which indicates how much power your generator can provide.
Conversion of Mechanical to Electrical Energy
The key to a generator's operation is the conversion of mechanical energy. When you turn on the engine, it starts creating mechanical energy by rotating a shaft.
This shaft is connected to the rotor, which is inside a coil of wire. As the rotor spins, it moves through a magnetic field. This movement transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy. It's like turning a crank to generate power, only much more efficient!
Role of Electromagnetic Induction
Understanding electromagnetic induction is crucial for grasping how generators work. When the rotor spins in the magnetic field, it causes electrons in the wire to move. This movement creates an electric current.
Electromagnetic induction happens because of the relationship between electricity and magnetism. When you change the magnetic field around a conductor, it induces a flow of electric current. This principle is the backbone of how many generators function, allowing them to provide you with reliable power during outages or heavy usage times.
Types of Home Generators
When choosing a home generator, it's important to understand the differences between types available. Each generator type has unique features that cater to specific needs. Here's a closer look at standby, portable, and inverter generators.
Standby Generators Explained
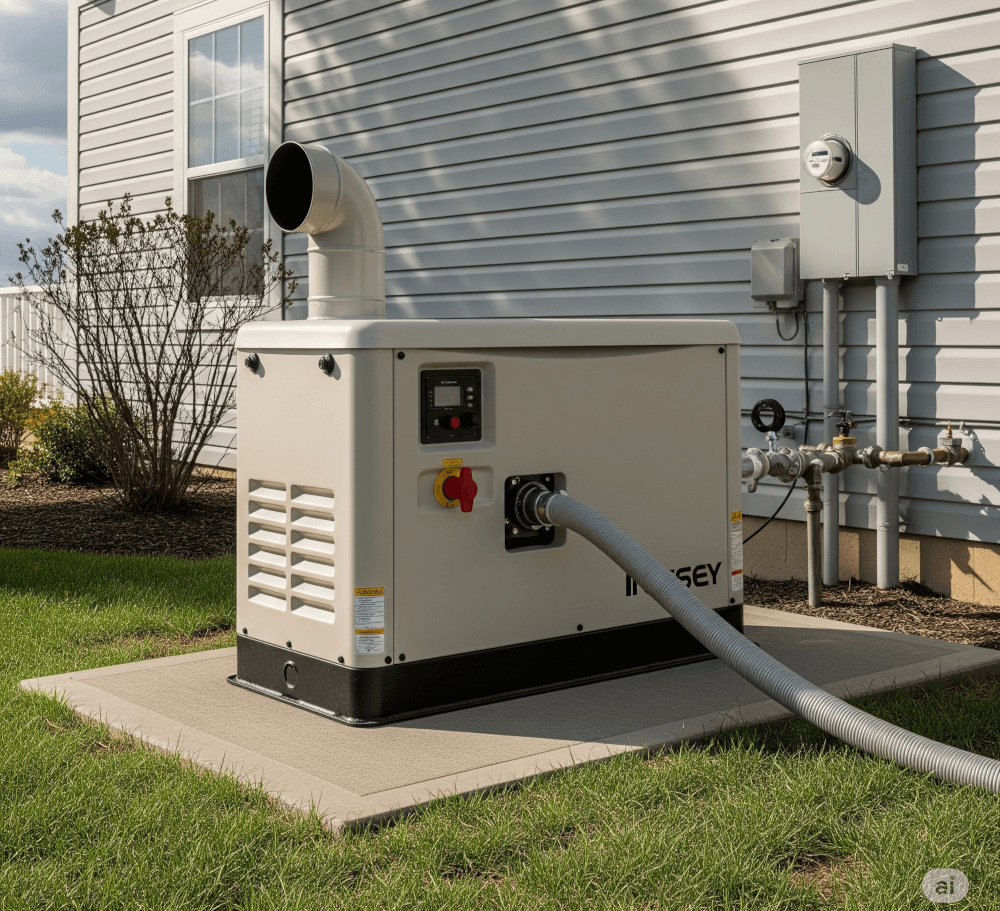
Standby generators are a reliable option for home power supply. These generators automatically turn on during a power outage, providing seamless electricity to your home.
Key features:
- Permanent Installation: They are installed outside your home, much like central air conditioning units.
- Automatic Transfer Switch: This feature automatically disconnects your home from the grid and connects to the generator.
- Fuel Sources: Standby generators typically run on natural gas or propane.
This type is ideal for homeowners who want uninterrupted power during outages, especially in areas with frequent power interruptions.
Portable Generators and Their Uses
Portable generators are versatile and easy to move. They are perfect for various situations, from outdoor events to home emergencies.
Benefits include:
- Ease of Use: You can easily transport them wherever you need power.
- Power Output: Most portable generators can provide 1,000 to 10,000 watts, sufficient to run essential appliances.
- Fuel Options: They often run on gasoline, making them accessible for temporary setups.
You might use a portable generator during camping trips or in emergencies when the main power supply is down. Just remember to set it up outdoors to avoid carbon monoxide buildup.
Understanding Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are known for their quiet operation and efficiency. They produce clean power that is safe for sensitive electronics.
Characteristics:
- Technology: Inverter generators convert AC power to DC and back to AC, ensuring a steady flow of electricity.
- Fuel Efficiency: These generators consume less fuel compared to traditional models, making them cost-effective over time.
- Noise Level: They are designed to run more quietly, usually at lower decibels than other generator types.
If you're looking for a generator to power sensitive devices like laptops and mobile phones, inverter generators are a great choice. Their compact nature also makes them easy to store.
Key Differences Between Generator Types
Understanding the differences between standby, portable, and inverter generators is crucial.
| Feature | Standby Generators | Portable Generators | Inverter Generators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Installation | Permanent | Temporary | Portable |
| Automatic Start | Yes | No | No |
| Fuel Sources | Natural Gas/Propane | Gasoline | Gasoline or Propane |
| Noise Level | Moderate | Moderate to Loud | Quiet |
| Best For | Long-term outages | Short-term use | Sensitive electronics |
Consider your needs and environment when choosing the right generator type. Each serves different purposes and has distinct advantages.
How Generators Operate During Power Outages
When the power goes out, you need a reliable solution to keep your home running smoothly. Generators are designed to provide backup power quickly and efficiently. They can activate automatically or require manual operation to keep your essential appliances running during an outage.
Automatic Activation and Transfer Switches
Many modern generators come with an automatic transfer switch (ATS). This switch detects the loss of utility power within seconds. When the outage occurs, the ATS signals the generator to start up.
Once the generator runs, the ATS transfers your home's electrical circuits from the utility supply to generator power. This means you don't have to do anything; the system takes care of it for you.
Automatic systems minimize the downtime during power outages, making them an excellent choice for those who want uninterrupted power.
Manual Transfer Switch Operation
Not all generators have automatic systems. If you have a manual transfer switch, you will need to activate the generator yourself. First, make sure the generator is filled with fuel and ready to go.
When the power goes out, switch off the main utility breaker. This prevents backfeeding, which can jeopardize safety. Next, start the generator and connect it to the transfer switch. Then, you can transfer power to specific circuits in your home, providing backup for lights and appliances as needed.
A manual transfer switch is a bit more hands-on but is still reliable during outages.
Supplying Backup Power to the Home
Once your generator is activated, it begins supplying backup power to your home. It can typically handle essential circuits like lights, refrigerators, and heating systems, depending on the generator's size.
For optimal use, you should prioritize which appliances need power. Make a list of essentials and manage usage to prevent overload. Most generators use either gas, propane, or natural gas as fuel sources.
Selecting the right fuel type can impact efficiency and ease of operation.
Keep in mind that routine maintenance is key to keeping your generator running smoothly, ensuring it's ready when you need it most.
Components of a Home Generator
Understanding the key parts of a home generator helps you appreciate how they work. Each component serves a specific role to keep your home powered during outages. Let's break down some essential elements.
Engine and Fuel System Overview
The engine is the heart of your generator. It converts fuel into mechanical energy. You can find engines powered by natural gas, propane, or gasoline.
The fuel system delivers the right amount of fuel to the engine. It includes components like the fuel tank, fuel lines, and filters. Maintaining a clean fuel supply is important for smooth operation. Regularly check the fuel lines for leaks and clogs.
Efficient fuel systems ensure that your generator runs effectively and provides reliable power when you need it most. Also, different fuels can influence the generator's performance and how long it can operate before needing a refill.
The Alternator's Function
The alternator is crucial because it transforms mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. This process makes it possible to power your home appliances.
Inside the alternator, you'll find a rotor and a stator. The rotor spins and creates a magnetic field. The stator captures this energy and converts it into electricity.
This component is key for maintaining a steady flow of power. Variations in speed can lead to fluctuations in output, so it's vital for the alternator to run smoothly. If issues arise, it can affect how well your generator functions.
Exhaust System and Safety Features
The exhaust system channels harmful gases out of the generator. It's vital for preventing dangerous fumes like carbon monoxide from entering your home.
Components of the exhaust system include pipes, mufflers, and catalytic converters. These parts help reduce noise and filter out toxins.
Safety features are equally important. Many generators have automatic shutdowns triggered by low oil levels or overheating. These features protect your generator and your home. Always ensure that the exhaust system is well maintained to keep everything running safely and efficiently.
Control Panel and Monitoring
The control panel allows you to operate your generator easily. It usually has switches, knobs, and gauges that show important information, such as voltage and frequency.
Monitoring systems give real-time data on your generator's performance. You can often find hour meters to track usage and maintenance schedules.
User-friendly designs make it easier for you to manage your generator effectively. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the controls to ensure you can respond quickly during a power outage. Regular checks on the control panel help in identifying potential issues early.
Safety Considerations When Using Generators at Home
Using generators at home can help during power outages but comes with safety risks. This section highlights crucial tips to ensure your safety while using these appliances.
Preventing Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless and odorless gas that can be deadly. When using a generator, make sure you are aware of the risks.
- Never use a generator indoors: Always place it outside, at least 20 feet from your home and away from any windows or doors.
- Install CO detectors: Place these devices in your home to alert you to CO levels.
- Recognize symptoms: Headaches, dizziness, and confusion can indicate CO exposure. If you see these signs, get outdoors immediately.
Regularly check your CO detectors to ensure they work. Replace batteries as needed to keep your family safe.
Proper Placement and Ventilation
Correct placement and ventilation of your generator are vital for safety. Here are some important tips:
- Choose an open area: Set up your generator in a well-ventilated space to avoid CO build-up.
- Avoid puddles: Keep the generator away from water to reduce electric shock risks.
- Use extension cords thoughtfully: If you need to run cords into your house, use heavy-duty cords rated for outdoor use.
Remember, maintaining proper distance from your home and ensuring ample ventilation can significantly reduce hazards. Prioritize safety every time you use your generator.
Factors Affecting Generator Selection and Cost
Choosing a generator for your home involves several key factors. Understanding power needs, comparing costs, and considering installation and maintenance will help you make the best choice for your situation.
Determining Power Needs
First, assess your power requirements. Think about the essential appliances and systems you want to run during an outage. Common items include:
- Refrigerator
- Heating/Cooling Systems
- Lights
- Electronics
You can use a power calculator or consult with a professional to estimate the wattage needed. Most generators list their wattage capacity. Make sure that the generator you select can handle your peak power demand, which is usually higher when starting appliances.

Comparing Generator Cost
Generator costs can vary widely based on type and features. Here are the main types you might consider:
- Portable Generators: Typically range from $400 to $1,200.
- Standby Generators: Usually cost between $2,000 and $6,000, including installation.
- Inverter Generators: Generally fall between $600 and $3,000.
Additional features like fuel type (gasoline, propane, or diesel) and noise level can affect the price. Make a list of what features are most important to you. This list will help you stay within your budget while meeting your needs.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Installation can add to your total costs. Standby generators often need a professional for setup, which can cost $500 to $1,500. Portable generators might just require simple hookups.
Maintenance is also critical for reliable operation. Regular checks, oil changes, and battery maintenance will ensure your generator works when needed. Budget for regular maintenance costs, which can be about $100 to $300 annually, depending on the type and frequency of use.
Taking all these factors into account will lead to better choices for your home's power needs.
Published 8/4/25